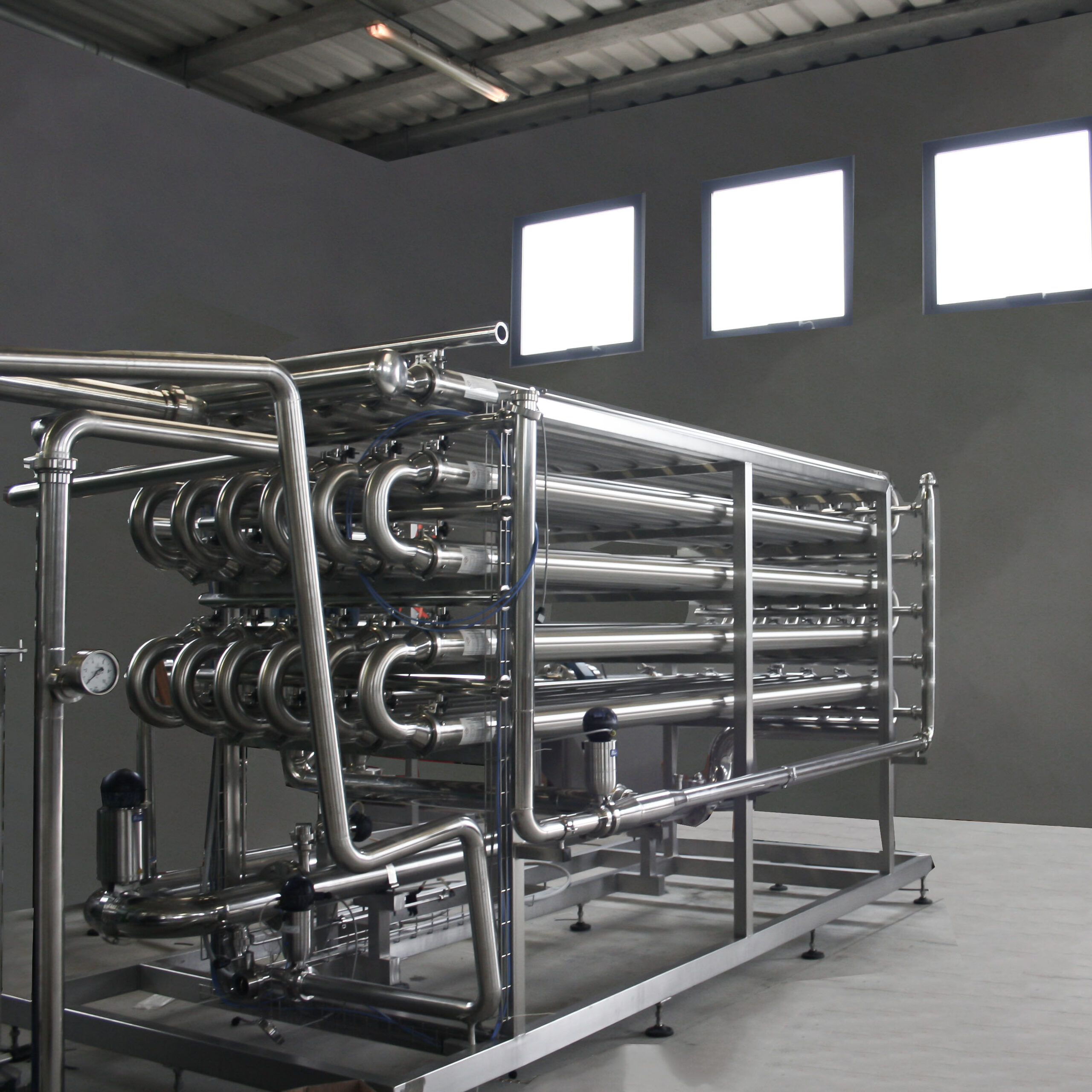
This technology is based on the use of semi-permeable membranes that can act as a selective barrier.
Membranes are essential in applications where suspended or dissolved particles need to be separated.
Their ability to separate components of different molecular weights makes them indispensable tools in situations where turbidity of fluids is essential, unlike nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes that are involved in the separation of dissolved molecules.
Applications:
- Clarification and clarification of liquids
- Colour concentration
- Soda recovery
- Water purification
- Protein isolation concentration
- Reduction of salt content
- Protein standardisation
- Reuse of water within the plant
- Waste treatment
Types of molecular separation
- Microfiltration
- Ultrafiltration
- Nanofiltration
- Reverse Osmosis
Advantages:
- Improved product quality
- Physical filtration without external additives
- Regenerability and durability
- Automation and labour
- Recovery of treatment and disposal costs